- Protection from predators such as wasps.
- Protection from predators such as badgers
- Protection from the weather
- Storage location for honey and pollen
- Nursery in which to raise young.
- Not too big- difficult to keep at right temperature.
- Not too small - they need space to grow
- Easy to ventilate - for temperature and humidity control.
- Easy to remove the honey without killing all the bees.
- Easy to check the hive for disease and pests.
- We can determine where is convenient for us to keep bees.
- The hive can be at a height suitable for us.
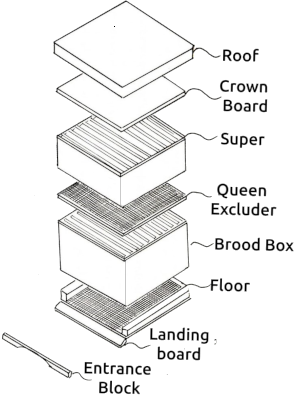
What is a hive - from the top down?
- Roof- to keep the rain off and heat in.
- Crown Board- to help keep the hive at a constant temperature.
- Super- where the honey is stored.
- Queen Excluder- to keep the queen out of the supers.
- Brood Box- the nursery for rearing bees and string food
- Floor- has an entrance for the bees
- Hive Stand- to put the hive at a suitable height.
Roof
- Very top layer -usually a wooden frame with a galvanised steel cover.
- It telescopes over the hive to keep out rain.
- Raised to allows ventilation above the crown board.
- First thing to come off when doing an inspection.
- Sits just below the lid on the top super.
- Thin sheet of wood with one or two holes.
- Holes allow you to feed bees in winter
- Put a one way "door" over holes to make a clearer board.
- Where the bees store the honey.
- There may be one or more supers on the hive.
- The super is an empty box with a ledges on each side from which hang the frames.
- The queen is the only one who lays eggs (normally).
- The queen is fatter than the other bees
- Queen excluder has slots to allow other bees through
- The queen cannot get through the excluder
- All the eggs are laid in the brood chamber.
- There are no eggs in the super where we collect honey from.
- Honey is not mixed with eggs and larvae
- Brood box is where the queen stays
- Queen lays eggs in the cells in the brood box
- Sometimes uses a brood box and a super for the queen
- This is known as a "brood and a half".
- Once we used solid wooden floors.
- Bees were warmer but then came Varroa.
- Now use mesh floors.
- Varroa that fall off bees fall out of the hive.
- Mesh floors also aid ventilation in the hive.
- A stand which raised the hive up from the ground.
- Keeps the hive is away from the damp ground.
- It saves you having to bend quite as far when inspecting the hive.
- Could be a small pile of concrete building blocks.
- Could be a couple of pallets
- Could be a proper wooden stand.
- I use concrete blocks - they do not rot.
